
Bookkeeping tasks include maintaining ledgers, income summary recording sales, and reconciling bank statements, which lay the groundwork for accurate Accounting. Because their reports are regularly scrutinized by oversight agencies, accountants are required to adhere to a uniform set of accounting standards. These rules specify how to record income, expenditures, assets, and losses, so that auditors have an objective view of the organization’s financial health. An accountant is a professional with a bachelor’s degree who provides financial advice, tax planning and bookkeeping services.

What is accounting?
Some explanatory notes should be given so as to make the information more understandable. It is generally not concerned with the accounting of individual business entities and is not based on generally accepted accounting principles. In short, we can say that accounting is the language of business by which all the financial and other information are communicated to various interested parties. Accounting is critical for groups and individuals and operate as the basis of economic selection-making and compliance. By providing accurate facts and insights, Accounting drives organisational success and guarantees transparency and duty in every financial transaction. A subset of managerial Accounting focuses on calculating and managing costs related to products and services to optimise profitability.
- At larger companies, there might be sizable finance departments guided by a unified accounting manual with dozens of employees.
- The ARPL is a coalition of various advanced professional groups including engineers, accountants, and architects.
- It is concerned with the interpretation of accounting information to guide the management for future planning, decision-making, control, etc.
- Accounting is used by business entities for keeping records of their money or financial transactions.
- Luca Pacioli is considered “The Father of Accounting and Bookkeeping” due to his contributions to the development of accounting as a profession.
- Much of the reporting of such information is voluntary, especially in the United States.
Following accounting standards
- Accounting provides information for all these purposes through the maintenance of data, the analysis and interpretation of these data, and the preparation of various kinds of reports.
- The Government is interested in the financial statements of business enterprise on account of taxation, labour and corporate laws.
- Bookkeeping tasks include maintaining ledgers, recording sales, and reconciling bank statements, which lay the groundwork for accurate Accounting.
- Business owners should be able to enter transactions, reconcile accounts and interpret financial statements accurately.
For example, when goods are purchased for cash, there is a movement of goods from the seller to the buyer and a movement of cash from buyer to the seller. Transactions may be external (between a business entity and a second party, e.g., goods sold on credit to Hari or internal (do not involve a second party, e.g., depreciation charged on the machinery). Therefore, all transactions are events but all events are not transactions. A transaction is a complete action, to an expected or possible future action.

Principles of Taxation (PTX)
This document summarizes historical performance and includes forward-looking information. “the art of recording, classifying, and summarizing in a significant manner and Keep Records for Small Business in terms of money, transactions and events which are, in part at least of financial character, and interpreting the results thereof.” Analysis and Interpretation The financial information or data as recorded in the books of an account must further be analyzed and interpreted so to draw useful conclusions. Thus, analysis of accounting information will help the management to assess in the performance of the business operations and forming future plans also.

Related Articles
In addition, accounting makes it possible to create financial projections to plan for the future and anticipate sales and expenses. Without accounting, it would be incredibly difficult to gauge your business’s performance and whether it’s on track to meet its goals and obligations. Trade creditors, bankers and other lending institutions would like to be satisfied that they will be paid on time. Banks and other lending agencies rely heavily upon accounting statements for determining the acceptability of a loan application. The Accounting definition is given by the American Institute of Certified Public Accountants (‘AICPA’) clearly brings out the meaning of accounting.

- If volume of sales of the products is high and the number of transactions of the business is very high, it is impossible to keep all these transactions in the mind of a businessman.
- Relevant information helps improve predictions of future events, confirms the outcome of a previous prediction, and should be available before a decision is made.
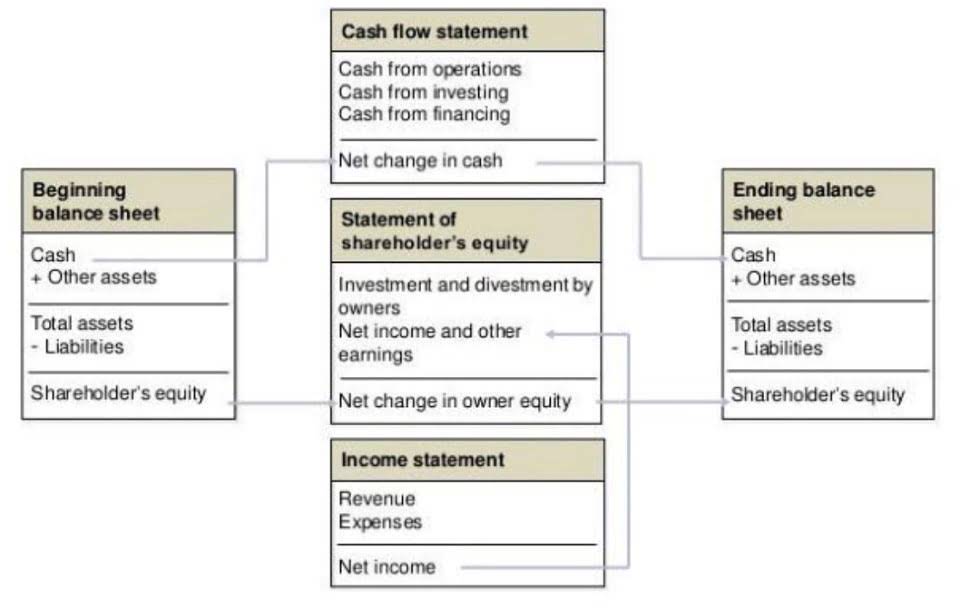
- This allows you to generate crucial financial statements, such as a balance sheet, cash flow statement, and profit and loss report.
- The reports generated by various streams of accounting, such as cost accounting and managerial accounting, are invaluable in helping management make informed business decisions.
Foreign companies must comply with tax what is accounting guidance in the countries in which they must file a return. These four largest accounting firms (Ernst & Young, KPMG, PricewaterhouseCoopers, Deloitte) conduct audit, consulting, tax advisory, and other services. These firms, along with many other smaller firms, comprise the public accounting realm that generally advises financial and tax accounting.